Multiganged / Tandem Potentiometers
In singleturn and multiturn variants
Guide Multiganged Potentiometers
Index
Basic questions about potentiometers? Here you will find the answers
Redundant potentiometers
The failure of a single, non-redundant sensor signal can lead to machine downtime and even hazardous situations. Redundant systems can detect a faulty sensor signal by comparing the signals. If there is a discrepancy, it often has a mechanical or electrical cause. In most cases it is a cable break and not a sensor fault. We therefore recommend the use of separate, high quality cable harnesses or wiring.
Redundant systems are used when it is advantageous to the application or when required by regulations. They are most commonly used to achieve the following objectives:
Increase machine availability or reduce downtime
The probability of all sensor signals failing at the same time is significantly reduced in redundant systems. By increasing the number of "gangs", the probability of failure can be minimized. In the event of a failure, it is not always necessary to shut down a system immediately. This ensures that, despite the disturbed signal, no major damage to property or even personal injury is caused.
Overall increase in operational safety
Due to the critical nature of the application, the machine is immediately shut down in the event of a fault. Redundancy allows for controlled shutdown. Examples of this can be found in vehicles and moving machines, e.g. when used in joysticks and control levers.
Rated power and temperature
The potentiometers are arranged in a row on a shaft. The resistors are not far apart. This means that the heat generated by the dissipation of each unit has an effect on the temperature of the neighbouring units. The maximum permissible nominal load of each resistive element or individual potentiometer segment is reduced as shown in the diagram.

These specifications are at ambient temperature. If the potentiometers are to be used at higher temperatures, the rated power must be reduced.
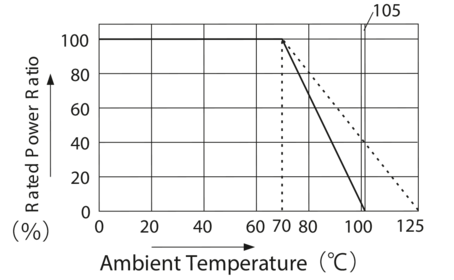
*This graph does not apply to the oil-filled potentiometers
Product customizations
In principle, the same product adaptations are available for the tandem versions as for the non-tandem versions: Special resistances, rear shafts, centre taps, linearity tolerances and shaft geometry adaptations, as well as bushing and servo flange versions. It is also possible to equip tandem potentiometers with different resistances or linearity tolerances for each sub-unit. However, these multi-turn potentiometers are used in rare special applications where the signal conditioning electronics require it.
Please note that tandem versions are not available for all series. For example, axial pins prevent the mounting of a second sensor segment. Please contact us if you have any questions regarding feasibility and special product adaptations. We will be happy to advise you.
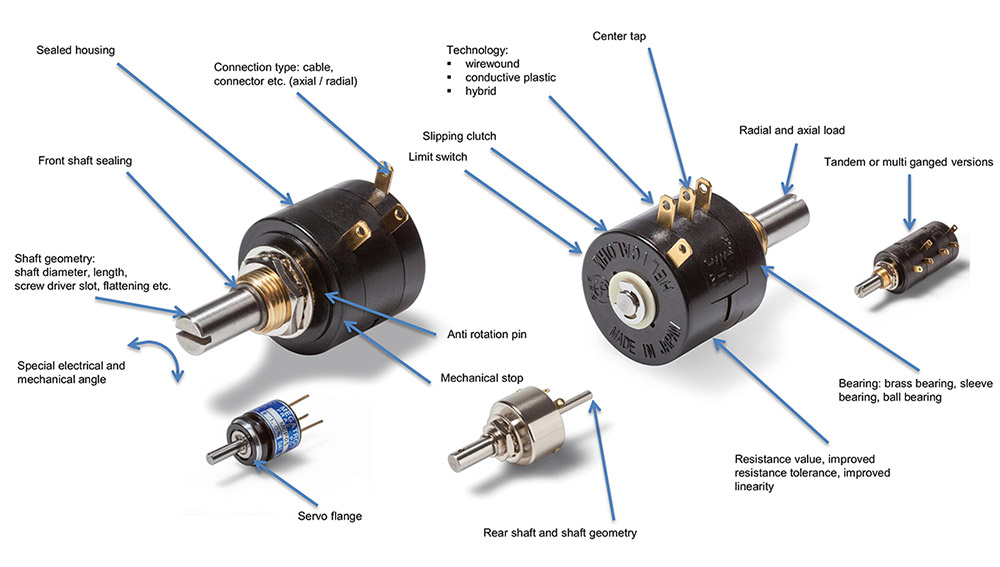
Multigang potentiometers are used in safety-critical applications where redundant connections and/or galvanically isolated signals are required. Several potentiometers are connected in a row as segments on one shaft. Tandem versions (2 units) are most commonly used. For very high safety requirements, up to 10 units in a row (10-turn potentiometers) can be implemented as single-turn or multi-turn versions.
The ability to select a specific resistance value, resistance tolerance or linearity for each gang makes multi-gang potentiometers complex and multi-functional components. In addition, depending on the type of potentiometer, all other options such as rear shaft, shaft adaptations, centre tap and limit switches are available.
MEGATRON is your specialist for the optimum technological product integration into your application. With quality products and high delivery reliability, we support you throughout the entire life cycle of your application. Our aim is to provide each customer with the best product for their application.
 EN
EN DE
DE ES
ES FR
FR PT
PT IT
IT